In the world of modern medicine, CT scans with contrast have become a common diagnostic tool. These scans are invaluable for their ability to reveal intricate details within the human body, allowing doctors to make more accurate diagnoses. However, for many patients, undergoing a scan with contrast can raise concerns, particularly related to Fatigue After CT Scan and potential side effects.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what happens during a CT scan with contrast, the reasons behind post-scan fatigue, and how to manage it.
What Is a CT Scan with Contrast?
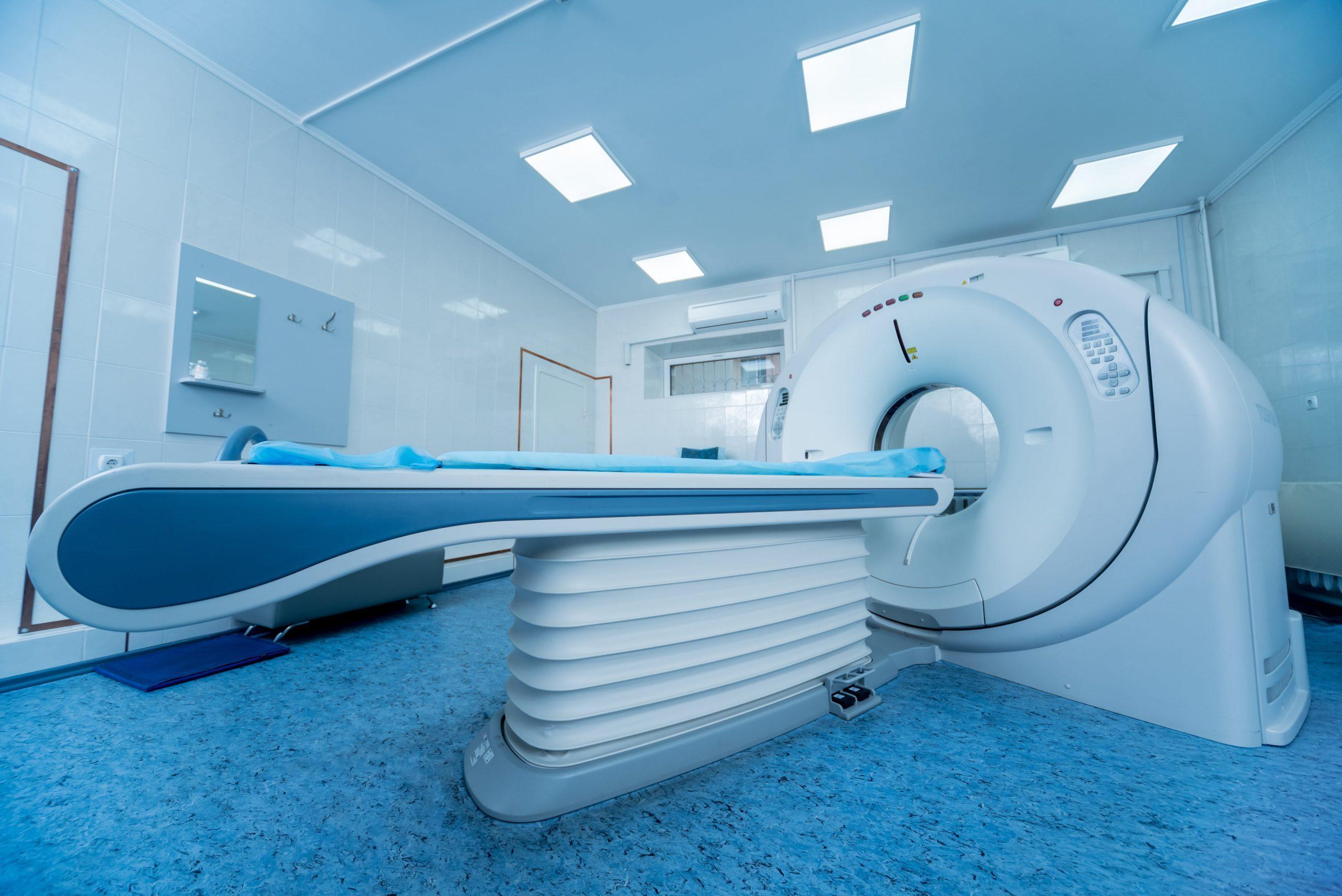
A CT scan with contrast, also known as a contrast-enhanced CT scan, is a medical imaging procedure used to obtain detailed images of the inside of the body. It involves the use of contrast agents, typically iodine-based, to enhance the visibility of blood vessels and certain body structures. The contrast material is administered either orally or intravenously, depending on the specific area being examined.
CT Scan Process
During the procedure, the patient lies on a specialized table that moves through a doughnut-shaped CT scanner. X-ray beams are used to capture multiple cross-sectional images, which are then reconstructed into detailed, 3D representations of the internal organs and tissues. This allows physicians to identify abnormalities, such as tumors, vascular issues, or internal injuries.
Why Fatigue After a CT Scan with Contrast?
The Role of Contrast Agents
Post-scan fatigue can be attributed to several factors, with contrast agents playing a significant role. These agents help highlight specific areas, but they can also put a temporary strain on the body. The body processes and eliminates these agents over time, and the process can lead to feelings of tiredness.
(Note: Contrast agents have evolved significantly in recent years, improving both safety and patient comfort. Traditionally, iodine-based contrast materials were ionic and high-osmolarity, which could cause more noticeable side effects like fatigue, nausea, or warmth during injection.
As of 2025, most medical facilities use non-ionic, low-osmolarity contrast agents. These newer formulations are gentler on the body, reducing the likelihood of adverse reactions while still providing clear, detailed images.)
Dehydration
Another common reason for fatigue after a CT scan with contrast is dehydration. Patients are often required to abstain from eating or drinking before the procedure, leading to a potential decrease in overall hydration levels. Dehydration can result in tiredness and discomfort post-scan.
Stress and Anxiety
The anticipation of a medical procedure like an emergency CT scan can trigger stress and anxiety, which may persist even after the scan is completed. This emotional strain can contribute to fatigue.
Coping with Post-Scan Fatigue
Here are some effective strategies to alleviate post-scan fatigue:
Hydration
The contrast agents used in CT scans are eventually filtered out by the kidneys and expelled from the body through urine. Ensuring an adequate intake of fluids can help expedite this process. Consider drinking water, clear juices, or herbal teas. Staying well-hydrated not only assists in flushing out the contrast agents but also prevents the development of complications related to dehydration.
Rest and Relaxation
After a CT scan with contrast, your body needs time to recuperate. Rest is essential for the recovery process. Opt for light activities such as reading, watching a movie, or simply lying down to rest. Avoid strenuous physical activities immediately after the scan. While a short nap might be beneficial, be mindful not to oversleep, as this can disrupt your regular sleep schedule.
Healthy Diet Before CT Scan
Consuming the right foods can help replenish your energy levels and support your body’s healing processes. Include a variety of foods in your diet, such as:
- Fruits: Fruits are rich in vitamins and natural sugars, providing a quick energy boost.
- Vegetables: Vegetables offer essential nutrients and antioxidants that aid in recovery.
- Lean Proteins: Sources like chicken, fish, and legumes can help rebuild and repair body tissues.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Foods like whole grains and starchy vegetables can provide sustained energy.
Avoid heavy or greasy meals, as they may cause discomfort or indigestion. Instead, focus on lighter, easily digestible options. Also, consider discussing your dietary choices with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Medication (Under Medical Supervision)
In some cases, physicians may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-nausea medications to manage any discomfort or side effects from the contrast agents. It’s crucial to take these medications under medical supervision and follow the prescribed dosage instructions carefully. If you experience any adverse effects, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Communication with Healthcare Provider
Maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider is paramount. If you experience severe or persistent symptoms, such as severe fatigue, unusual pain, or allergic reactions, do not hesitate to reach out to your medical team. They can provide guidance, address your concerns, and adjust your post-scan care plan if necessary.
Monitor Your Symptoms:
Keep a mental note of how you feel in the hours and days after the scan. Mild fatigue or a slight headache should fade within 24-48 hours. If they don’t, or if you notice symptoms like rash, itching, or shortness of breath, contact your provider—these could signal a rare allergic reaction.
Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine:
These can dehydrate you further or interfere with restful sleep, slowing your recovery. Stick to water or herbal teas instead.
Who’s Most Affected by Post-Scan Fatigue?
While post-scan fatigue can affect anyone undergoing a CT scan with contrast, certain groups may experience it more intensely or require extra care:
- Elderly Patients: Aging kidneys may process contrast agents more slowly, leading to prolonged fatigue. Older adults might also have lower baseline energy levels, amplifying the effect.
- Individuals with Kidney Conditions: Those with reduced kidney function (e.g., chronic kidney disease) face a higher risk of fatigue, as their bodies take longer to filter out the contrast material. Recent guidelines emphasize pre- and post-scan hydration for these patients to minimize strain.
- People with Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like diabetes or heart disease can make the body more sensitive to the temporary stress of contrast agents, increasing tiredness.
First-Time Patients: Anxiety about the procedure can heighten fatigue, especially for those unfamiliar with CT scans.
Conclusion
While post-scan fatigue is a common occurrence after a CT scan with contrast, understanding the reasons behind it and taking appropriate measures can help alleviate discomfort. Remember that it’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance on post-scan care to ensure a smooth recovery.
By following these guidelines and giving your body the attention it needs, you can mitigate post-scan fatigue and return to your daily activities with minimal disruption. If you have further questions or concerns about CT scans with contrast, don’t hesitate to consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
FAQs
1. Why do I feel tired after a CT scan with contrast?
Fatigue can result from the body processing the contrast agent, dehydration from fasting, or stress about the procedure. The kidneys work to filter out the iodine-based contrast, which may temporarily drain your energy, especially if hydration levels are low.
- How long does fatigue last after a CT scan with contrast?
For most people, fatigue fades within 24-48 hours as the body clears the contrast. If it persists longer or worsens, consult your healthcare provider, as it could signal an underlying issue like reduced kidney function.
- Can I prevent fatigue after a CT scan with contrast?
Yes, you can reduce fatigue by hydrating well before and after the scan (unless instructed otherwise), resting afterward, and eating a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to replenish energy.
- Are there side effects from the contrast agent that cause fatigue?
Modern non-ionic contrast agents are gentler, but mild side effects like fatigue, warmth, or nausea can still occur as your body metabolizes them. Severe reactions are rare but require immediate medical attention if they happen.
- Who is most likely to feel fatigued after a CT scan with contrast?
Elderly patients, those with kidney conditions, chronic illnesses like diabetes, or first-timers anxious about the scan are more prone to fatigue. Tailored prep and recovery steps can help these groups feel better faster.