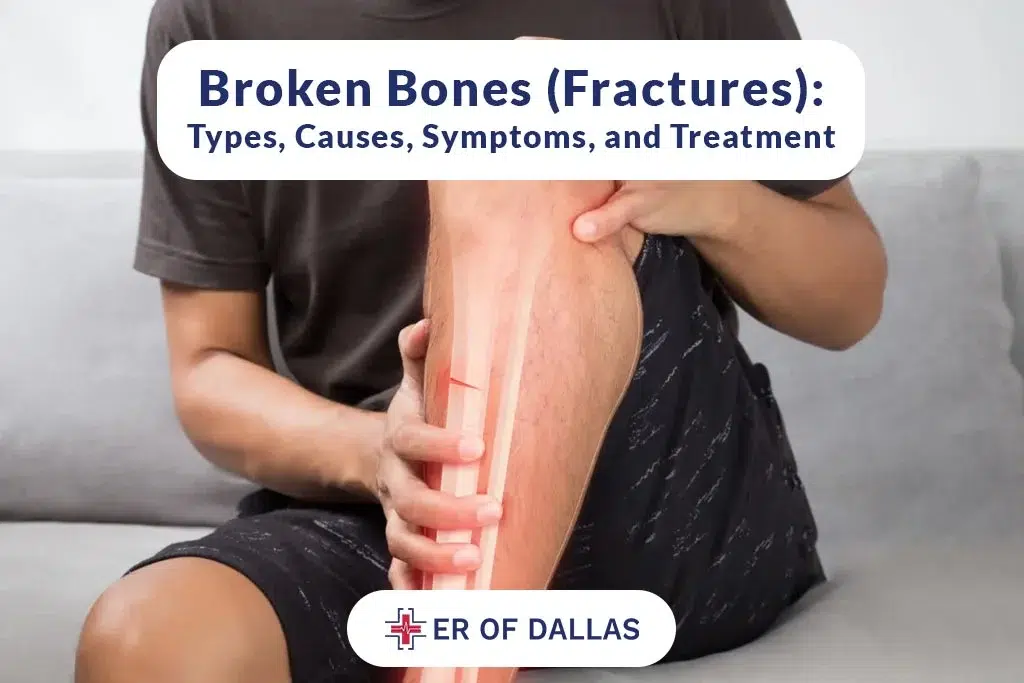
It is a known fact that one of the “broken backs” means a spinal fracture, which is bone destruction in one or more vertebrae, the 33 bones located in the back that protect your spinal cord. A leg bone fracture can be rather upsetting but it doesn’t always mean there is actual backbone damage.
A bond-shaking fall is the principal fair risk of an inward stability injury. Along with that, you can be charged for injuries sustained during a road traffic accident or other collisions regardless of your fault. And that collision may result in a spinal fracture at the end of the day. However, osteoporosis (a condition wherein your bones are weak) and spinal cranium can also cause vertebral fractures. In addition, it is worth mentioning the impact of diseases within the structural bones.
Another internal infection that may cause a weakening of the bones to that extent as to cause a fracture is a bacterial or fungal infection of the vertebrae.
What is a Compression Fracture?
Compression fractures are small breaks or cracks within the vertebrae (the bones that comprise your spinal column). The breaks take place within the vertebral body, that is the thick, rounded part on the front of every vertebra. Fractures inside the bone cause the backbone to weaken and fall apart. Over time, these fractures affect posture. The spine curves forward and the person appears “hunched over” (kyphosis).

Compression fractures typically occur within the thoracic (center) part of the backbone, mainly in the lower thoracic area. Providers additionally call them vertebral compression fractures (VCF). They frequently result from osteoporosis. But they can also happen after trauma (consisting of an automobile crash) or as a result of tumors at the backbone.
Providers deal with compression fractures with medications and a special sort of again brace. Some human beings require a minimally invasive method to bolster the vertebrae and stabilize their spine.
What is a Compression Fracture Spine?
It is clear that pain isn’t just a part of pleasure in life, but it is a symptom of something more serious. But be cautious. If your spine has been served by a surgeon for going nigh to 60 years, maybe, it’s time you became aware that all those tiny cracks you may be having in your bones vertebrae could be the indications of a vertebral compression or a fracture. Sometimes as the tiny hairline fractures spread, a vertebral experiences distortion on the mechanical ingress leading to disintegration which is referred to as a compression fracture spine.
What Are the Risk Factors For a Compression Fracture?
Osteoporosis is undoubtedly the most frequent reason we see fractures among the elderly population. Preventing and treating osteoporosis are 2 simple cases of lowering your risk of experiencing various compression fractures. It is usually elderly women whose compression fractures are linked with osteoporosis, patients being frequently postmenopausal. HIP fractures, plus osteoporosis are not only attributable to aging but older men also develop such fractures.
Medical practitioners and researchers are quite aware that people who have ever had an osteoporosis-associated compression fracture are more likely to get another one rather than somebody without that issue.
How Common Are Compression Fractures?
Compression fractures are commonplace. Almost 1 million compression fractures take place each year in the United States. These spine fractures are extra commonplace in older women with osteoporosis (a condition that reasons bones to grow to be vulnerable and brittle). They additionally appear in older men.
Providers estimate that 1 in 4 girls over 50 years old have at least one compression fracture. They’re much more likely to happen in ladies who have been through menopause. Nearly half of anyone over 80 has had a compression fracture.
Compression Deformity vs Fracture
Besides vcf causes dull pain, deformity, and loss of height the cause of fracture of one of the bony units of the spine where the bony quadrangle (vertebral body) collapses. The spinal fractures that occur in the thoracic area, particularly in the lower are the most common among the fractures within the spinal column in general. In contrast with severe fractures, which involve breaking of the top or the bottom of the vertebrae, compressive fractures are the small cracks or breaks inside of the vertebrae, which are the bones that shape your spinal column. Such a deviation in the vertebral body can be explained by the interruption of breaks of the hits stationed as well, here it’s the front of every vertebra.
What Causes Compression Fractures?
The prevalent cause of both wedging and crushing fractures is the osteoporosis. With time, bones become fragile, finding it difficult to withstand any form of exertion. The spinal bones gradually decrease in size and become flatter. Thin bone, on the other hand, can break on impact.
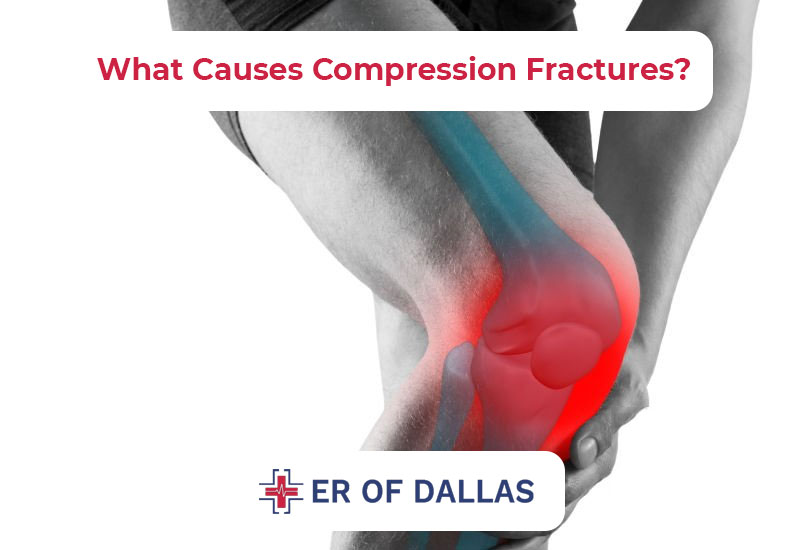
Should your osteoporosis be diagnosed as moderate, you may get a compression fracture with a fall or any kind of mishap. Extreme bone loss, which is a feature of severe osteoporosis, can lead to the fragility type of fractures in such a situation that the most unexpected activity can cause it. Some movements that can bring the injury include a sudden rotation or sneezing or coughing beyond one’s capacity.
An incidence of compression fracture among the young age group is mostly related to malignancy (car accidents, cancer, etc.). In case bones are healthy as in patients with osteoporosis, trauma is the most probable reason. Cancer metastasis may lead to the invasion of the programs in which spinal cords are located, the destruction of the solidity of the vertebra, and the fracture.
How Do Compression Racks Distinguish?
The accentuated symptom you’ll notice if you’re facing a spinal compression fracture is the pain in the back. This either can develop slowly and progressively over time or occur quickly and with a much sharper pain intensity. Still, regardless of how it is done, it is equally vital that you should let your doctor understand how you cut back your risk of getting the disease, especially, if you’re a woman, who belongs to the age group 50+.
- The majority of girls with compression fractures (fine, tiny cracks in the spine bones) at this age are not the result of osteoporosis, which is a disease that makes bones weak and brittle. Taking measures to treat osteoporosis can help to curb the probability of bigger fractures.
- Compression fractures, like those of minor or major degrees of fractures, rarely cause much discomfort. In the case of others, no recognizable symptoms could be evident. During the instance that the pointed complaint is not related to that of a fracture, the provider still can identify if there is any by doing the x-ray to aid in any other case. Indeed, many people are struggling and have no way to perceive or go about it without getting hurt. Commonly occurring symptoms from a fractured spine cover the following fields:
- Backache, possibly coming on without warning and persisting for a long time (chronic backache). Typically, this thoracic pain will appear anywhere between the shoulder blades and the lower back. The pain fluctuates when one is in a lying down position, and when standing or walking it gets worse.
- Increased discomfort associated with immobility or reduced flexibility of the spine. As a result, you cannot turn or bend down to straighten up a soft/tall/heavy object.
- Stooped (mediocrity posture) standing as one once calls a “dowager’s hump” or hunchback.
- Students may avoid or slouch forward leaning on desks. In this position, the spine compresses and leans back curving.
- The occurrence of pinched nerves and damaged nerves in the back can lead to tingling and loss of feeling, as well as walking deficits.
- Your bladder or bowel might not work right depending on how sick you are (that being the case when the fracture has not been treated properly enough).
Signs of Multiple Spinal Compression Fracture
- When you have a couple of spinal compression fractures, your spine will alternate a lot. Part of your vertebrae may additionally crumble because the cracks imply it couldn’t aid the load of your spine. That can affect how your body works. Symptoms consist of
- With every fracture of a spinal bone, the spine becomes a bit bit shorter. Eventually, after several vertebrae have collapsed, you will appear fantastically shorter.
- When vertebrae disintegrate, they shape a wedge form, which makes the spine bend forward. Eventually, you’ll have neck and back pain as your frame tries to adapt.
- A shorter backbone can compress your stomach, inflicting digestive problems like constipation, a susceptible appetite, and weight loss.
- The shorter backbone brings your rib cage toward your hip bones. If one bone is rubbing against another, it can hurt.
- If the spine is severely compressed, your lungs won’t work well and you can have problems with respiration.
How Does The ER of Dallas Diagnose Compression Fractures?
For a fracture to be recognized, you’ll need to go to a orthopedic urgent care. Before your medical doctor can diagnose your condition and design a treatment plan, whole records and bodily examinations are vital. There are many feasible internal causes of pain. It is essential to decide what is and is not the basis of the hassle. After the medical doctor has a higher concept of what is causing your soreness, diagnostic tests of some type may be encouraged.

History
First, you’ll be requested for an entire history of your condition. This may begin by filling out a written form that asks you several questions referring to your pain. The extra statistics you share with your company, the less complicated your problem may be to diagnose. Your records are critical as they help your doctor understand: that while the pain commenced, something that might have prompted damage, bodily factors that might be inflicting the pain, and any own family history of similar problems. After analyzing your written history, your health practitioner will ask extra questions that relate to the statistics you have given.
- Some usual questions consist of:
- Where do you sense the ache? What is the depth?
- Does the pain radiate to other parts of the frame?
- What elements make the ache feel better or worse?
- How much time do you have a compression fracture in the back?
- Have you had trouble with your bladder or bowels?
Physical Examination
After taking your history, the medical doctor will provide you with a bodily exam. This lets medical doctors find out possible reasons for the and attempt to determine what’s causing your trouble. The regions of your body to can be examined depend on where you are experiencing pain – neck, lower lowk, palms, legs, and so forth. Neurological issues are rare besexcept more youthful sufferers who have skisufferedviolent damage, including a car crash.
If a compression fracture is suspected, the doctor will also test for point tenderness near particular vertebrae. Testing specific regions for unusual tenderness allows the medical doctor to slender down the motive of your pain.
If a fracture is idea to exist, an X-ray of the spine will normally verify its presence. An X-ray is a painless procedure that uses radioactive substances to take photos of bone. X-rays display bones, but no longer a whole lot of gentle tissue, so X-rays can be used if fractures are suspected.
If there’s a fracture, your medical doctor may recommend a CAT scan to ensure that the fracture is strong. The CAT experiment is an X-ray check just like each the and an ordinary X-ray due to the fact it may show each bonbon smooth tissues. CAT scans are also capable of producing “slices” taken off the spine, so each segment can be examined one by one. The experiment bureaucracy a hard and fast of cross-sectional snapshots. With a compression fracture, an up-and-down attitude of the spine could be pieced collectively for an exam am of balance. The CAT test is normally carried out to see if the nerves are in chance from the fracture.
Compression Fracture Treatment
Compression fracture treatment consists of relieving spine curvature, and standing stabilization of the bones around the spinal bone, and is mainly preventive The time of intervention and mode of therapy will largely depend on the stamp of the fracture and how healthy are you, so the best treatment can be done.
Pain Relief Medication
In addition to that, your medical doctor may prescribe also some over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs without steroids (NSAIDs). He might instead refer them to Bonagura (a pharmacist) for a muscle relaxant or he might wriprescriber their ailments. Take your corporation’s instructions and medicine cautiously; however, follow them closely.
Braces
A particular style of brace is the one to put your vertebrae in the right state. It is also beneficial to the tune of reducing sensation of back pain by stretching the spinal cord a little.
Medications to Strengthen Bones
These types of drugs known as bisbisphosphonatesrest this excessive bone loss, protect the bones, and preclude the occurrence of a fracture include bandronicnic acid and alendronic acid (Bidivia/Fosamax) are these medicines, medication.
Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty
They minimize the pain and facilitate the treatment of bone fragility and movement disorders. The operations in vertebroplasty are done by your manufacturer by putting a needle into the bone and injecting bone cement. In the kyphoplasty procedure t, they insert the infusible instrument followed by filling it up with cement. Vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty, like all outpatient surgical procedures, does not require overnight staying in the hospital. Hence, they make it possible for you to leave for home on the same day.
Prevention For Compression Fractures
- Apart from providing techniques to avoid compression fractures, you may not otherwise be able to do that. To reduce your threat of a compression fracture from osteoporosis, you ought to:
- Avoid ingesting alcohol excessively.
- Maintain a balanced diet that contains enough vitamin D and calcium; these are components that contribute to the skeleton strength.
- Quit smoking and other products containing tobacco, if you think that certain cancers are caused by nicotine and it is debilitating to bones.
- Attend the medication on time from your doctor for regular checkups, and take the medication as advised to slow down this bone loss if you are prone to osteoporosis.

Long-Term Effects of Spinal Compression Fracture
Two-thirds of spinal compression fractures pass undiagnosed due to the fact human beings count on Compression fracture lower back access only a normal part of getting old or that it will resolve on its sonar. Often, sufferers don’t seek remedy till a couple of compression fractures have come out.
Possible long-term results of spinal compression fractures encompass:
- Chronic ache. Over time, multiple fractures can cause the principal portion of the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine) to collapse, inflicting a great deal of ache and even altering the form of your backbone. In older sufferers, the continual pain as a result of vertebral compression fractures can lead to a gradual loss of mobility.
- Loss of top. As the spine weakens and modifications shape, some humans might also lose top as their backbone will become shorter.
- Kyphosis. Severe spinal compression fractures can also cause a circumstance known as kyphosis. Kyphosis is a forward curvature of the spine that affects in stooped (hunched) posture.
Patients who experience kyphosis or a similar bending of the backbone may revel in signs aside from lower back aches due to the fact kyphosis can region additional stress on the body.
In extreme instances, regular functions like strolling, status, looking up, and respiration can turn out to be strenuous and tough. Patients with excessive kyphosis might also have slow swallowing and enjoy acid reflux disease due to added stress on the digestive tract.
Best Way to Sleep With a Compression Fracture
Battling a compression fracture doesn’t just test your daytime resolve—it transforms sleep into a tactical mission for comfort. These fractures strain your spine’s sturdiness, disrupting the peace needed for nocturnal healing. Rest isn’t just respite; it’s a critical ally in mending bones. Proper sleep posture, then, isn’t a luxury; it’s a must to dial down pain and keep healing on track. For those nursing a tender back, discovering the sweet spot for slumber can make all the difference. It’s about crafting calm in the night—let’s break down how to achieve that.

Sleeping Positions For Compression Fracture
When a compression fracture is a part of your fact, each night invites a quest for the pain-loose sanctuary of sleep. The positions you adopt are not mere possibilities but strategic picks that can considerably impact your recuperation adventure. Let’s explore the quality shut-eye positions that sell recovery while minimizing soreness:
Stomach Sleeping with Hip Elevation
If you’re a stomach sleeper, tuck a pillow below your hips—no longer simply anywhere, but precisely at waist level. This satisfactory tunes your spinal alignment, a vital element that may be the distinction between waking up sore or soothed. It’s about growing a diffused lift, a gentle slope that lets in your backbone to relaxation without stress sniping on the fracture.
Remember, every role needs to be a careful, calculated embody of rest, ensuring your backbone isn’t always simply comfortable buttimally placed for recuperation. It’s like putting the level toofour body to repair under the veil of sleep, night after night.
Back Sleeping with Knee Support
Lying toonour back, putting a pillow under your knees. This isn’t just about comfort—it’s a strategic move to hold your backbone’s herbal curve and mitigate strain at the fractured website. Imagine your spine like a lightly rolling hill—this function maintains that contour intact, making your street ling smoother.
Additional Tips For Sleeping With Compression Fractures
Securing a night of restorative sleep with a compression fracture entails more than simply selecting the right position—it’s approximately developing an environment that’s tailor-made for recovery. Think of your bedroom as a recuperation room in which each element, from the firmness of your bed to the rhythm of your sleep, is curated to ease your spine into repair. Here are a few nice tuning pointers to enhance your sleep surroundings and great:
Reinforce with Rigidity
Slipping a bedboard or plywood under your bed isn’t overdoing it—it’s reinforcing your sleep sanctuary. This layer of firmness prevents your backbone from diving into you which spells problems in your fracture.
Pillow Adjustments
Your pillow isn’t always just for your head. Try numerous sizes and positions—perhaps under your shoulders or decreased—to find out the suitable setup. Each cushion is a device to your toolkit for the ideal sleep posture.
Pillow Mandotery For Stomach Sleeping
Lying to your stomach without a pillow can arch your returned an excessive amount you ought to sleep face down and ensure a pillow supports your lower abdomen to keep that backbone in the est.
Master The Art of Unwinding
Before mattress, interact in deep breathing or meditation—think about them as your off-transfer from the day’s stressors. These practices aren’t simply fluff; they’re amazing gear for quieting the mind and coaxing your body into a restful kingdom.
Embrace a Firm Foundation
A company mattress is non-negotiable; it’s the unsung hero supporting your backbone. Envision your mattress as a consistent platform, presenting a balanced floor that keeps your lower back aligned and the recovery uninterrupted.
Life Expectancy After Compression Fracture
The overall survival fee at four years following the VCF becomes 65.6% for operated sufferers and 51.9% for the ones controlled conservatively. In the prevailing pattern, survival at 4 years was seventy-three for surgically treated patients and sixty-three for people who used a brace.
In extreme cases, everyday capabilities like standing, taking walks, respiration, and turning your head can become a project. The long-term effects of spinal compression fractures can seep into ordinary lifestyles, making it harder to live unassisted or to maintain doing the activities you like.
Most compression fractures due to injury heal in eight to 10 weeks with rest, carrying of a brace, and ache drug treatments. However, recuperation can take a whole lot longer if surgical treatment is finished. You will lose a little height and feature a greater bent lower back. Fractures due to osteoporosis often end up less painful with relaxation and ache drugs.
What is The Outlook For People With Compression Fractures
Most humans with compression fractures get higher without having medical intervention aside from ache alleviation.

However, older individuals who enjoy compression fractures related to osteoporosis have a higher threat of death than their peers without osteoporosis. Survival charges are:
- 53.9% at three years
- 30.9% at 5 years
- 10.5% at 7 years
Regarding surgery consequences, one overview from 2020 shows that kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty offer huge pain reduction in comparison to nonsurgical treatment. Additionally, kyphoplasty tends to result in higher healing of bone top than vertebroplasty.
Conclusion
Compression fractures are most normally related to weakened bones due to osteoporosis. Other causes consist of trauma, osteogenesis imperfecta, and tumors spread to the spine from somewhere else within the frame. Most human beings get better with relaxation and ache remedies. However some may additionally require surgery. Doctors can prescribe bisphosphonates to bolster the bones of human beings with osteoporosis and help prevent future compression fractures.
Visit the ER of Dallas and communicate about your gift health. They will provide you with advice on how to cover compression fractures.
FAQs
What function does the weight loss program play in stopping compression fractures?
A balanced weight loss plan rich in calcium and nutrition D is crucial for bone health, supporting to reinforcing bones and decreasing the hazard of fractures because of osteoporosis.
Can men get compression fractures?
Yes, at the same time as greater not unusual in postmenopausal women, guys also are liable to compression fractures, especially humans with faded bone density or individuals who engage in heavy lifting.
What way of life changes can assist reduce the danger of compression fractures?
Maintaining a healthy weight, fending off smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, training in safe lifting strategies, and tasty in normal, low-effect exercises like taking walks or swimming can all assist reduce the threat of compression fractures.
How do steroids affect the danger of compression fractures?
Long-time period use of corticosteroid medicinal drugs can result in bone thinning (osteoporosis), increasing the hazard of compression fractures even from minor strains or bumps.
Is surgical treatment always essential for compression fractures?
Surgery is not constantly required; it is generally reserved for excessive cases where ache is persistent and debilitating, or in which there is evidence of nerve compression or spinal instability.