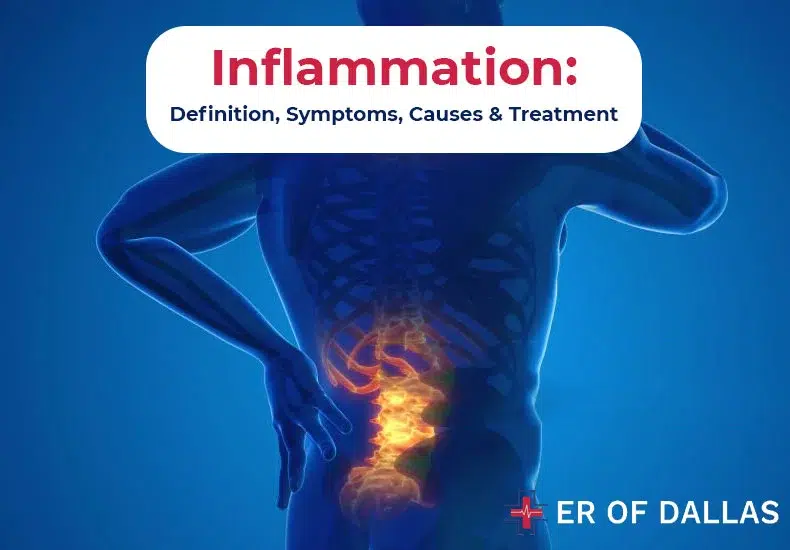
The body may send cells to defend itself against an alien entity, such as a virus, irritant, or thorn. Pathogens are creatures, such as bacteria, viruses, and other things, that cause infections.
Now and then, the body perceives its tissues or cells as harmful. This reaction may lead to autoimmune diseases, such as type 1 diabetes. Inflammation can play a part in many chronic illnesses. Examples of metabolic syndrome include type 2 diabetes, obesity, and heart disease.
Individuals with these disorders often have higher inflammatory markers in their bodies.
This article will teach you more about the causes, symptoms, and treatments of inflammation.
What Is Inflammation?
Inflammation is an essential part of your body’s healing process. It occurs when inflammatory cells travel to the place of an injury or foreign body, like bacteria. If inflammatory cells stay too long, it may lead to chronic inflammation.

Your body uses inflammation to defend against infections caused by bacteria, viruses, and other foreign invaders. White blood cells and the substances they produce are responsible for this process.
However, when there are no external threats to repel, your body’s defensive mechanism, the immune system, causes inflammation in certain illnesses, such as arthritis. Your immune system reacts to certain autoimmune disorders as though normal tissues are abnormal or contaminated, which damages them. This reaction is inflammatory. The effect can be pain, swelling, bruising, or redness. However, inflammation also has an impact on invisible bodily processes.
Types of Inflammation
There are 2 types of inflammation:
Acute Inflammation
This type, which is the reaction to abrupt bodily trauma like cutting your finger, is perhaps more known to you. Your body sends inflammatory cells to the cut to aid in healing. These cells initiate the process of healing. Depending on your health, acute inflammation could last anywhere from a few hours to a few days.
Chronic Inflammation
Your body keeps producing inflammatory cells even in the absence of external threats. For instance, in rheumatoid arthritis, the tissues of the joints are attacked by inflammatory cells and chemicals, resulting in intermittent inflammation. This may result in excruciating joint discomfort. Long-term chronic inflammation can persist for several months or even years.
What Are The Symptoms of Inflammation
Acute inflammation symptoms:
- Skin that has been flushed at the injury site.
- Growing.
- Sensitivity or pain.
- Warmth.
Chronic inflammation symptoms may be harder to spot than acute inflammation symptoms. Signs of chronic inflammation can include:
- Chest pain
Abdominal pain - Fever
- Mouth soreness
- Skin rash
- Depression
- Mood disorders
- Weight gain or weight loss
- Joint pain, and Insomnia
What Are the Causes of Inflammation
The following are the most typical causes of persistent inflammation:

- Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus, in which the body targets healthy tissue.
- Exposure to harmful substances, including industrial chemicals or pollution.
- Untreated acute inflammation resulting from a wound or infection.
- Instances of acute inflammation that recur.
- Autoinflammatory diseases, such as recurring fever syndromes, are caused by abnormalities in the cells responsible for inhibiting inflammation.
Inflammation Treatment
Inflammatory illnesses can be treated with drugs, rest, physical activity, and joint replacement surgery. Your age, the medications you take, the nature of your illness, the severity of your symptoms, and your general health will all play a role in your treatment strategy.
The purpose of the therapy is to:
Correct, manage, or decelerate the course of the illness
Steer clear of or alter activities that exacerbate pain.
Reduce joint tension by employing canes, braces, or splints as required.
Reduce discomfort by taking anti-inflammatories and painkillers.
Maintain muscle strength and joint mobility with physical therapy
Medications
Numerous medications can reduce inflammation, edema, and discomfort. Additionally, they might lessen or stop inflammatory illnesses. Physicians usually recommend more than one. Among the drugs are:
- Hydroxychloroquine an antimalarial medication.
- Aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Prednisone is an example of a corticosteroid
- Biological drugs such as abatacept, adalimumab, certolizumab, etanercept, infliximab, golimumab, rituximab, and tocilizumab
- DMARDs, such as azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, leflunomide, methotrexate, and sulfasalazine, are other medications that treat rheumatoid arthritis
A few of them are also used to avoid organ rejection following a transplant or to treat ailments including cancer and inflammatory bowel disease. However, compared to when they are given for cancer treatment, “chemotherapy” drugs (such as methotrexate or cyclophosphamide) typically have lower dosages and a lower risk of adverse effects when used to treat inflammatory illnesses.
Surgery
If inflammation has seriously harmed your joints, you might require surgery. Typical practices consist of
- Arthroscopy. Your physician makes a few tiny incisions all around the injured joint. To mend rips, replace damaged tissue, or remove fragments of bone or cartilage, they insert thin devices.
- Arthrodesis. Bones can be permanently fused with pins or plates.
- Osteotomy. A portion of the bone close to a damaged joint is removed by your doctor.
- Synovectomy. If the synovium, the tissue lining the joint, becomes inflammatory or grows too much, it may be removed entirely or in part.
- Replacement of the joint. Your physician replaces a damaged joint with a ceramic, metal, or plastic prosthesis.
Home Remedies
Among the strategies to reduce chronic inflammation are:
- Engage in regular exercise.
- Give up smoking.
- Control your tension.
- Restrict your alcohol intake.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
Try taking the best supplements for inflammation like capsaicin, white willow bark, curcumin, green tea, or omega-3 fatty acids. Additional anti-inflammatory benefits of magnesium and vitamins B6, C, D, and E are also present. Consult your physician before beginning any supplement regimen.
What Are The 5 Worst Foods For Inflammation
It seems that most advice focuses on the best things to eat that reduce inflammation. Increasing these foods is just one aspect of the solution, though. It’s crucial to cut back on food ingredients that might be causing or exacerbating pre-existing inflammation in the body in addition to minimizing chronic inflammation.
Here are the top foods that aggravate inflammation along with tips on reducing them.
Processed Meats
The majority of processed meats, such as lunch meats, hot dogs, bacon, and pepperoni, are preserved using artificial nitrates and salt. Saturated fat content is also frequently high in certain meats. Regular use of processed meats has been associated with an increased risk of inflammation, which many believe is a result of both nitrates and saturated fats, according to a 2022 study published in the Journal of Nutrition.
How to reduce: The best suggestion is to reduce your entire consumption of processed meat because the science isn’t sure exactly which of the three sources of threat—nitrates, saturated fat, or processed meats altogether—is the main concern. If you do consume processed meats, choose “uncured” meats, which should indicate that salt was the only treatment applied to the meats rather than nitrates. Ingredients like celery juice, a natural source of nitrates, can be used in nitrate-free meats. Whether these are healthier than meats treated with artificial nitrates is still up for debate.
Refined Carbs
Consuming bread, pasta, white rice, and other high-carb foods made mostly of grains or refined flour causes the blood sugar to rise more quickly. Foods that have a higher blood sugar impact have been explicitly connected in a 2018 study published in the American Journal of Physiology to increased inflammation, which raises the risk of obesity, metabolic syndrome, Type 2 diabetes, and other inflammatory disorders.
How to reduce: When feasible, choose whole grains and products made entirely of whole grains. Additionally, keep in mind that complex carbohydrates aren’t only found in grains. Beans, peas, sweet potatoes, and other starchy vegetables that are strong in nutrients and fiber are good sources of them. Choosing whole grains over refined grains decreased body weight and inflammation in adults, according to a 2019 study.
Trans Fats
To extend the shelf life of processed foods, unsaturated lipids are chemically changed to form trans fats. However, trans fats may be even more detrimental to the body than saturated fats, which are present in red meat, cheese, and butter, according to a 2021 study that was published in Frontiers in Immunology. This is mostly because of the inflammatory response they cause in the body, which has been connected to long-term conditions like diabetes and heart disease.
How to reduce: Avoid items that include “hydrogenated” or “partially hydrogenated” oils in the ingredient list to avoid trans fats. While the FDA outlawed the inclusion of hydrogenated oils in packaged goods in 2018, certain cooking oils that are used to prepare fried and fast food items inherently contain trans fats. Try to eat those foods less frequently.
Highly Processed Food
In response to consumer demand for quick and easy food options, producers have increased the number of ready-to-eat meals and grab-and-go items they offer. However, this ease of use has a cost because artificial coloring, flavorings, preservatives, and other chemicals that aren’t naturally present in food are frequently added to these items to increase their shelf life or to enhance their flavor and look. The body might get irritated by any of these, leading to inflammation. Furthermore, the body can be reactive to these foreign particles if there is already some inflammation present, which could worsen the situation by causing more inflammation.
How to reduce: Quick can still be healthy if you choose convenience foods with little to no processing. Make sure you start by looking at the ingredient list to accomplish this. Generally speaking, a shorter list is preferable. Next, try to identify the ingredients. Asking yourself “Would I make this at home from a recipe, would most of these ingredients be in it?” is a useful tactic when perusing the ingredients list. If not, search again.
Extra Amount of Omega – 6s
The majority of us refer to mono- and polyunsaturated fats as “healthy” fats. These fats are composed of various ratios of fatty acids, of which omega-6s and omega-3s are two essential types. According to a 2021 study that was published in the Journal of Lipids, the majority of Americans consume far too much omega-6 fatty acids, partly as a result of the widespread usage of vegetable oils like corn, soybean, and sunflower in convenience and processed meals. Furthermore, it appears that we are significantly under consuming the potent anti-inflammatory omega-3 fatty acids. All in all, an imbalance results, which could be a factor in low-grade systemic inflammation.
How to reduce: First, aim to include fatty fish such as salmon, canned tuna, or mackerel in your weekly intake of omega-3s. You may also include walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds in your diet. Next, begin examining the oils you use in your cooking or eating. The key is to select oils with a larger amount of omega-3 fatty acids, such as extra virgin olive oil, avocado oil, walnut oil, flax oil, peanut oil, corn oil, and canola oil.
How to Use Essential Oils for Inflammation
Essential oils can be utilized in several ways to alleviate inflammation because they affect the entire body:

Diffusion: You can get an essential oil diffuser from Wal-Mart or CVS, as well as online. Particles of essential oil can spread directly into the air using a diffuser. Smelling it may aid in relaxation. This could be helpful if stress is the cause of your inflammation.
By mouth: Certain essential oil varieties are designed to be gargled, however they are uncommon. In a 2011 analysis, researchers discovered that using an essential oil mouthwash helped lessen gingivitis-related gum inflammation. Before attempting this procedure, make sure to speak with your physician. It is not recommended to ingest essential oils.
Massage: To help with pain and swelling reduction, apply diluted essential oil directly to the affected area.
FAQs
Does Inflammation Cause Weight Gain
Inflammation may contribute to weight gain through metabolic disruptions, insulin resistance, and hormonal imbalances, impacting body composition and health.
Vicks Vapor Rub Helps Inflammation
Vicks Vapor Rub is believed to help with inflammation as its menthol component has a cooling effect that can alleviate discomfort. Applied topically, it may temporarily ease muscle aches and joint pain, providing relief. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for persistent or severe inflammation issues.
Does Icy Hot Reduce Inflammation
Icy Hot primarily works as a topical analgesic, providing a cooling and warming sensation. While it may temporarily alleviate pain, it doesn’t directly reduce inflammation. Consult a healthcare professional for persistent inflammation issues, as Icy Hot is not a substitute for targeted anti-inflammatory treatments.
How Long Does Prednisolone Take To Work For Inflammation
The onset of action for prednisolone, a corticosteroid used to reduce inflammation, varies depending on the individual, the condition being treated, and the severity of inflammation. In some cases, improvement may be noticed within a few hours to a day, while in others, it may take several days to a week. It’s crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance on your specific condition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding inflammation is vital for managing overall health. Staying informed helps individuals make proactive health decisions, from recognizing symptoms to exploring treatment options. If you’re in the Dallas area and seeking immediate care, consider the ER of Dallas for prompt and professional assistance. Remember, timely intervention and a comprehensive approach to inflammation can significantly impact well-being. Stay informed, seek medical advice, and utilize accessible resources like the ER of Dallas to ensure a proactive and informed approach to inflammatory conditions.